As we proudly progress with another product update released today (refer digivizer.com) I am reflecting on what it takes to continue to grow and do more than just survive. With key outcomes that include launching our new product, now made affordable for every business, expansion into Asia, 30% of revenues earned overseas, and the launch of our gaming and esports specialisation in goto.game, it has taken a number of pivots for Digivizer to grow to where it is today.
Knowing how to survive by building a culture of learning and pivoting fast is essential because in the world of startups and early growth, nothing is for ever. As serial entrepreneur Steve Blank says in his book The Four Steps To The Epiphany, a startup is “a temporary organization used to search for a repeatable and scalable business model.” I think that’s true of most startups. It’s certainly been true of Digivizer.
We’ve learned, though, that to build out our ability to grow-fast in our organization, we have needed to build the capability to pivot quickly. If you do, you can thrive and change direction to take advantage of new opportunities, and move quickly away from slower growth, and from initiatives that don’t provide returns or suck up resources.
Let’s take a look at the journey so far.
Changing direction to move faster
We started Digivizer with a vision to build a technology company, initially to track all Australians on the social web. Early customers were larger enterprises that included a number of Australia’s banks, tech and telco companies. All loved the data, insights and input into strategy that Digivizer was able to provide. Understanding the digital footprint and behavior of their customers with context was used for the first time by many of these organizations.
The promise of overseas expansion beckoned early on. Australia represents just 0.33% percent of the world’s population. Our horizon was always global, even as a startup. Early engagements included for a global company, as one example, incorporating and analysing Chinese language within our analytics engine.
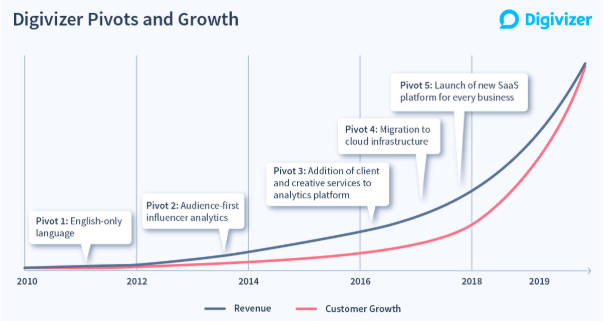
Our pivot history
However, the learning in the smaller (and younger) Digivizer led to the first in a number of pivots: the investment to support such a multi-language contract ultimately proved too high for a fast return that would also depend on local representation. To help scale Digivizer technology we decided to stop other language support (despite the lucrative contract) and focus only on English.
By this time, more organizations recognized the value of real-time insights. They wanted turn-key solutions, support in real-time decision-making, content and managed digital and social marketing programs, and measurement of performance in real-time.
Our second pivot was to build a creative services team centered on social community managers and creatives that could rapidly build, input and track performance within the Digivizer platform. This allowed us to bootstrap growth and product development off client creative services revenue, whilst providing a point of differentiation. We were not an agency because everything we did was based on our own data analytics engine, and we were not solely a technology company because we could action insights in real-ime with creative services. This saw sales doubling each year for the three years.
With our technology now able to identify social segmentation around what mattered and who people were following, pivot number three beckoned – in audience-first thinking. Identification of influencers within market segments, and adding the ability to engage, track and report on the impact of any influencer programs, offered the next opportunity for growth.
The underlying platform that had worked in our early history began to slow scalable growth, and to stretch precious resources. We had originally built our own data platform to take advantage of low comparative cost, only to see the costs of maintaining that platform becoming excessive. A migration to the cloud, not a decision we took lightly or one that was simple to execute, allowed us to focus on building our IP, changing the focus for our valuable engineering resources.
Our most-recent pivot takes us back to our original vision: to provide a way to help grow every business by helping them understand and make better decisions around their digital investment.
Whilst continuing to deliver creative solutions, we’ve now our brought our technology to companies of any and every size, including and especially SMBs and startups, with our SaaS product.
Tough decisions reap rewards
At the time, some of these decisions were hard to take, but the results speak for themselves: we have gone to market faster than we otherwise would have.
Pivoting need not be drastic, nor mean discarding years of strategy and work. Our pivots were not fundamental changes in our strategy, but they were in prioritization of resources and implementation plan. And while some were momentous at the time, they were made with care and were completely congruent to our vision. What became obvious is that hiring, developing and building capability around pivoting, and seizing new opportunities, fast becomes the true business competitive advantage. When we started there were about 20-30 players in the same space. Now there are just two of us left in Australia of those early players, and we do and offer very different products and solutions.
Lessons learned
In planning to pivot, as part of developing a strategy that will meet your image, you must also incorporate a people strategy flexible enough to accommodate change.
You need to understand what your customers actually need and ensure that’s what you deliver in a way that they see as being valuable.
Always seek to build on the learnings from the steps you’ve taken before, without being hidebound by the actual steps or sunk costs.
To pivot is more than not breaking your business: it is about seizing the moment as each opportunity presents.
This article also published on LinkedIn

 Original post seen on
Original post seen on 
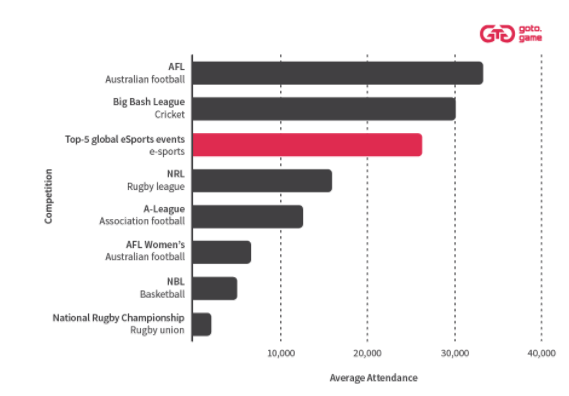
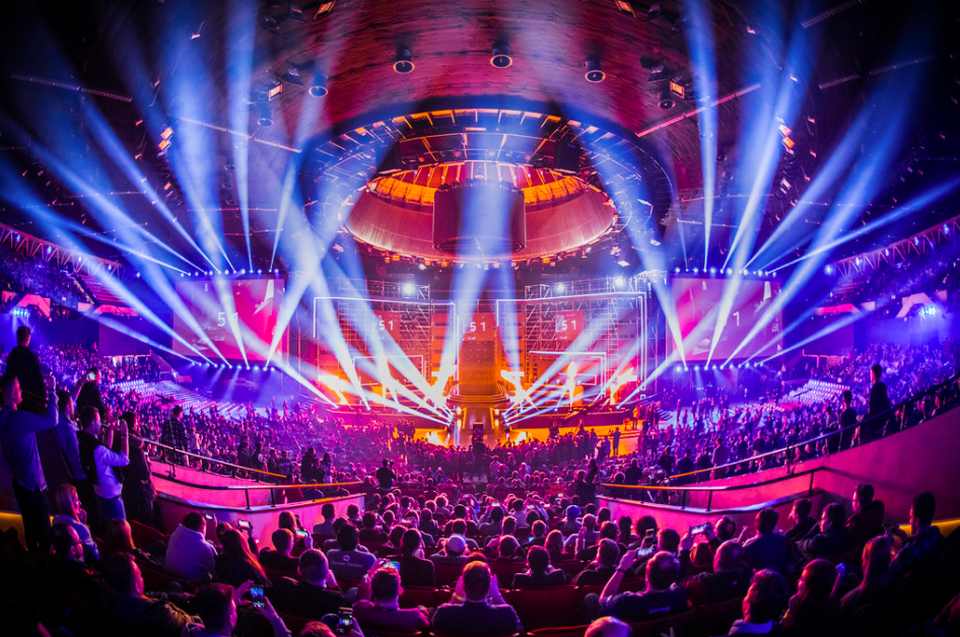
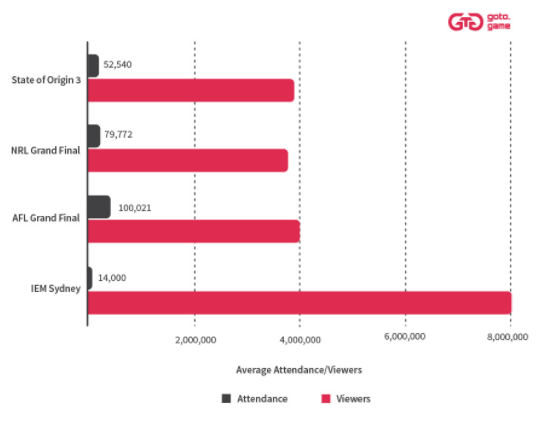 While care is needed with these comparisons – it’s not possible to break out how any people outside Australia watched the Australian sporting codes, nor the proportion of those who watched IEM output based here in Australia – one thing is clear: esports attract greater audiences and a larger number of overseas audiences. This is why we need to advocate early for our new stadiums to support these type of events and digital infrastructure and support required.
While care is needed with these comparisons – it’s not possible to break out how any people outside Australia watched the Australian sporting codes, nor the proportion of those who watched IEM output based here in Australia – one thing is clear: esports attract greater audiences and a larger number of overseas audiences. This is why we need to advocate early for our new stadiums to support these type of events and digital infrastructure and support required.

